Key takeaways
- Multiple well-known ICS attacks have been successful by gaining an initial foothold into the IT network, such as EKANS, Black Energy, and Havex
- Stage One of the ICS Cyber Kill Chain is network reconnaissance, and so IT/OT network segregation is critical
- Darktrace finds that many organizations’ networks have at least some level of IT/OT convergence
- Visibility across ICS infrastructure, actions, and commands provides a better picture into potentially malicious internal activity
IT & OT Convergence Threats
Shipping, manufacturing, and other forms of heavy industry are seeing an ever-increasing convergence of IT and OT systems with the growth in Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). At the same time, it remains critical to segment IT from OT networks, as the lack of segmentation could provide a malicious actor – either a hacker or rogue insider – easy access to pivot into the OT network.
High-profile attack campaigns such as Havex or Black Energy show traditional network security monitoring tools can be insufficient in preventing these intrusions. After the initial compromise, these ICS attacks progressed from IT to OT systems, showing that the convergence of IT and OT in cyber-physical ecosystems calls for technology that can understand how these two systems interact.
More recently, analysis of the EKANS ransomware revealed that attackers are attempting to use malware to actively disrupt OT as well as IT networks. The attack contained ICS processes on its ‘kill list,’ which allowed it to halt global manufacturing for large organizations like Honda.
More often than not, a lack of visibility is a major challenge in protecting critical ICS assets. Security specialists benefit when they have visibility over unusual or unexpected connections, or more crucially, when ICS commands are being sent by malicious actors attempting to perform industrial sabotage.
Investigation details
Darktrace analysts investigated the use of industrial protocols in the enterprise environments of various customers. The industries ranged from banking to government, retail to food manufacturing and beyond, and included companies with Industrial Control Systems that leverage Darktrace to defend their corporate networks.
In some cases, the security teams may not have been aware of IT/OT convergence within their enterprise environments. In other cases, the IT team may be aware of the ICS segments, but do not see them as a security priority because it does not fall directly within their remit.
The results revealed that hundreds of companies are using OT protocols in their enterprise environments, which suggests that IT/OT systems are not properly segmented. Specifically, Darktrace detected over 6,500 suspected instances of ICS protocol use across 1,000 environments. Note that this data was collected anonymously, only keeping track of the industry for analysis purposes.

The ICS protocol which was detected the most was BacNet, seen in approximately 75% of instances. BacNet is used in Building Management Systems, so it is not surprising that it is widely used across multiple industries and within corporate networks. It is likely the security teams are aware that their BMS is part of the enterprise network, but may not appreciate how its use of the BacNet OT protocol increases the attack surface for the business and can be a blind spot for security teams.
Core ICS protocols
Darktrace also detected ‘core’ ICS protocols, Modbus and CIP (Common Industrial Protocol). These are normally associated with traditional ICS industries such as manufacturing, oil and gas, robotics, and utilities, and provides further evidence of IT/OT convergence.
This increased IT/OT convergence creates new blind spots on the network and sets up new pathways to disruption. This offers opportunities for attackers, and the public are now increasingly aware of attacks that have pivoted from IT into OT.
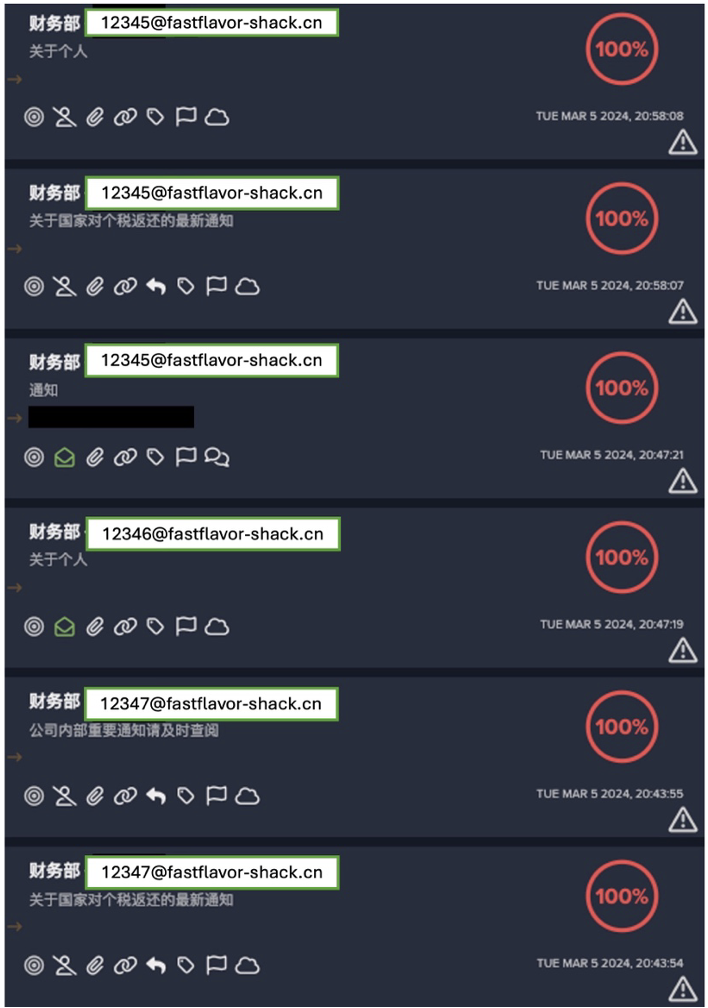
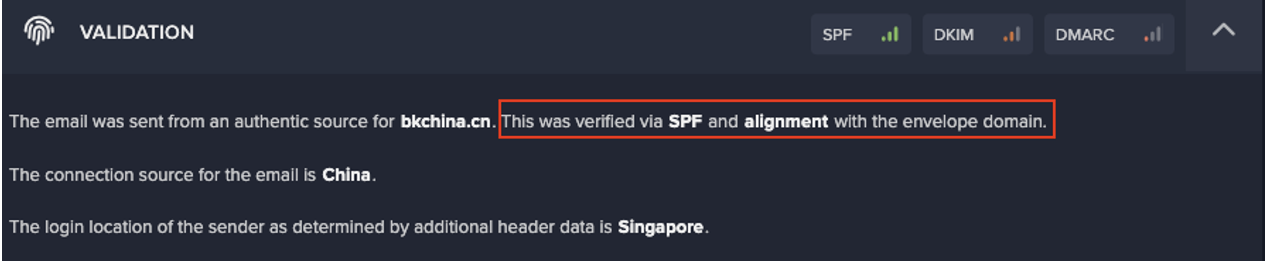
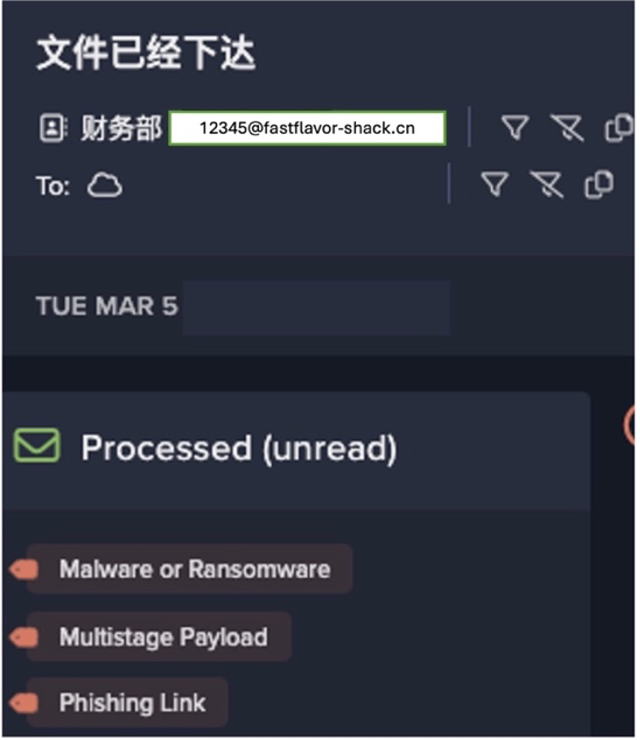
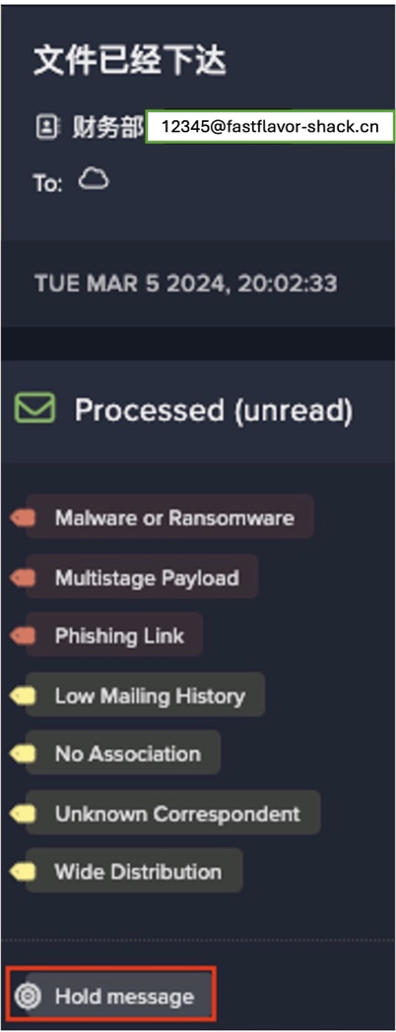
Improper segmentation between IT and OT systems can lead to highly unusual connections to ICS protocols. This can be seen in our recent analysis of industrial sabotage, with the timeline of the attack’s main events presented below.

This is just one example of an attack that began in IT systems before affecting OT. More high-profile attacks that follow this pattern are presented below:
EKANS ransomware
The recent EKANS attack involved a strain of ransomware with close links to the MEGACORTEX variant, which gained infamy following an attack on Honda’s global operations in June 2020. Like many ransomware variants, EKANS encrypts files in IT systems and demands ransom in order to unlock the infected machines. However, the malware also has the ability to kill ICS processes on infected hosts. Notably, it is the first public example of ransomware that can target ICS operations.
Havex
Havex utilized multiple attack vectors, including spear phishing, trojans, and infected vendor websites, often known as a ‘watering hole attack’. It targeted IT systems, Internet-connected workstations, or a combination of the two. With Havex, attackers leveraged lateral movement techniques to pivot into Level 3 of ICS networks. The attack’s motive was data exfiltration to a C2 server, likely as part of a government-backed espionage campaign.
Black Energy 3
Black Energy 3 favored macro-embedded MS Office documents delivered via spear phishing emails as attack vectors. Older variants of Black Energy targeted vulnerabilities in ICS HMIs (Human Machine Interfaces) which were connected to the Internet. The attack’s motive was industrial sabotage and is what was used against the Ukrainian electric grid in 2015, leading to power outages for over 225,000 civilians and requiring a switch to manual operations as substations were taken offline.
Lessons learned
Each of the attack campaigns detailed above was in some way enabled by IT/OT convergence. Attackers still favor targeting IT networks with their initial attack vectors, as IT networks have significantly more interaction with the Internet through emails, and various other interconnected technologies. Poor network segmentation allows attackers easy access to OT systems once an IT network has been compromised.
In all of these ICS cyber-attacks, devices deviated from their normal patterns of life at one or more points in the cyber kill chain. Indicators of compromise can include anything from new external connections, to network reconnaissance using active scanning, to lateral movement using privileged credentials, ICS reprogram commands, or ICS discovery requests. With proper enterprise-wide visibility, across both IT and OT systems, and security tools that are able to detect these deviations, a security team would be alerted to these compromises before an attacker could carry out their objectives.
Ultimately, visibility is crucial for cyber defenders to protect industrial property and processes. Darktrace/OT enables many Industrial Model Detections, a selection of which are listed below:
- Connexion anormale entre l'informatique et le SCI
- Multiple Failed Connections to OT Device
- Multiple New Action Commands
- Uncommon ICS Reprogram
- Suspicious Network Scanning Activity
- Unusual Broadcast from ICS PLC
- Unusual Admin RDP Session
It is clear that attackers continue to exploit increasing IT/OT convergence to carry out industrial sabotage. Still, as revealed by our analysis of our customer base, many organizations continue to unknowingly use ICS protocols in their corporate environments, both increasing their attack surface and creating dangerous blind spots. A new, holistic approach to cyber defense is needed – one that can reveal this convergence of IT and OT, provide visibility, and detect deviations indicative of emerging cyber-attacks against critical systems.
Thanks to Darktrace analyst Oakley Cox for his insights on the above investigation.